Year in Review (2024)
As the year 2024 is coming to an end, I have compiled my usual "reflections on the year".
As noted early this year (see here, here and here), this year marks the 25th year anniversary of my "professing career". This milestone, coupled with my kids all growing up and moving on with their own lives, has provoked some serious introspection in me in terms of thinking about the new and future career challenges I would like to undertake in the remaining years of my career.
I am keen to pursue novel opportunities for exploring both teaching and research at the intersection of biomedical science/ science communication and public policy, as well as political theory and ethics. I have substantive research projects already underway for the next 3 years, but also some longer term ideas for projects spanning the next 20+ years. At least in my own mind, I see the 25th year anniversary of my career as roughly the "mid-point" of my academic career, broadly defined. This may be overly optimistic but my enthusiasm about research and teaching show no signs of waning so I see the next quarter of a century as an incredible opportunity to address some really unique challenges and opportunities that humanity faces.
The major personal accomplishment for me this year, with respect to research, was the completion and publication of my new book Classics of Political Thought for Today: An Introduction, a book that was a quarter of a century in the making.
This year was also an eventful one for my research on geroscience and climate change, with a number of invitations to present my ideas which then provided the fuel to me writing some new work at the intersection of geroscience and climate science.
According to PubMed, 2024 is my most productive year for journal publications, at least for those dealing with biomedical issues. However this really reflects the happenstance that a bunch of things just happened to come out officially in print in the same calendar year. There are always "peak and trough" years for publications. The peak of this year is not something I could sustain year after year. Nonetheless, it certainly is a research year I feel sense of accomplishment about.
My journal publications that appeared in print this year are:
A few distinctive developments stand out to me about the past year. Firstly, I have learned to communicate complex ideas visually. This is a result of publishing a good deal of science journal articles that utilize visuals. I have been refining this skill set over the past 2 years or so, and I was surprised by how much I enjoy it, as well as how much I have learned from the process. Expressing ideas visually actually alters how one conceptualizes and communicates one's ideas and insights.
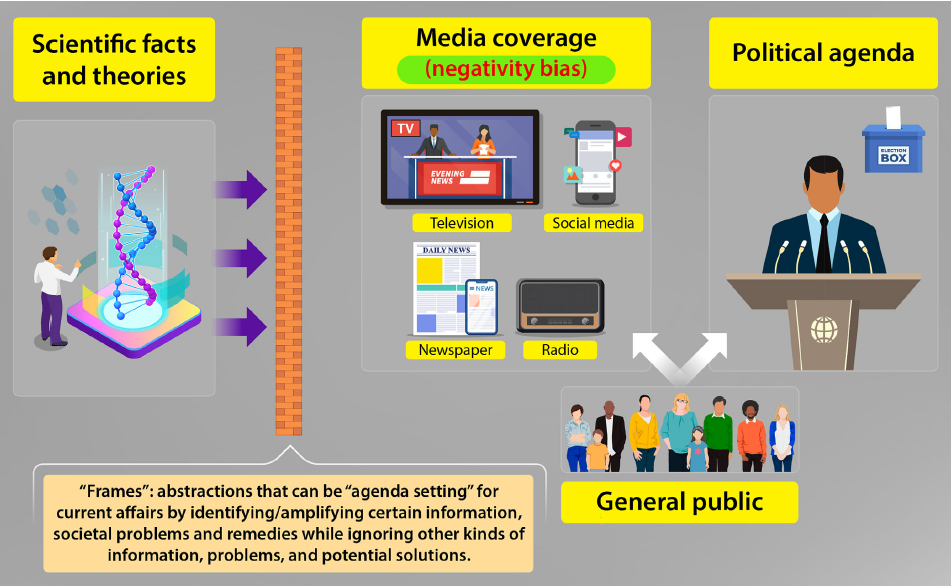
Here are my favorite visual images that appeared in print this year:
The image below is from the Open Science paper
Secondly, I had a few things posted online this year, which is novel for me. These include my inaugural Peacock lecture, my plenary lecture from RCCN workshop on “Climate Change and Aging" and an online presentation in the Royal Society's "Ecology and Evolution" seminar series. I was also invited to design a 25 minute video lecture on the ethics of geroscience for geroscientists which is not currently publicly accessible.
I look forward to the research developments of 2025!
Cheers,
Colin